
For example, yeast reproduces asexually through the method of budding. This developing bud detaches from the parent body and the daughter individual develops further.

These amoebules are released together when the conditions turn favourable.īudding − In this method, a bud develops as an outgrowth from parent body.

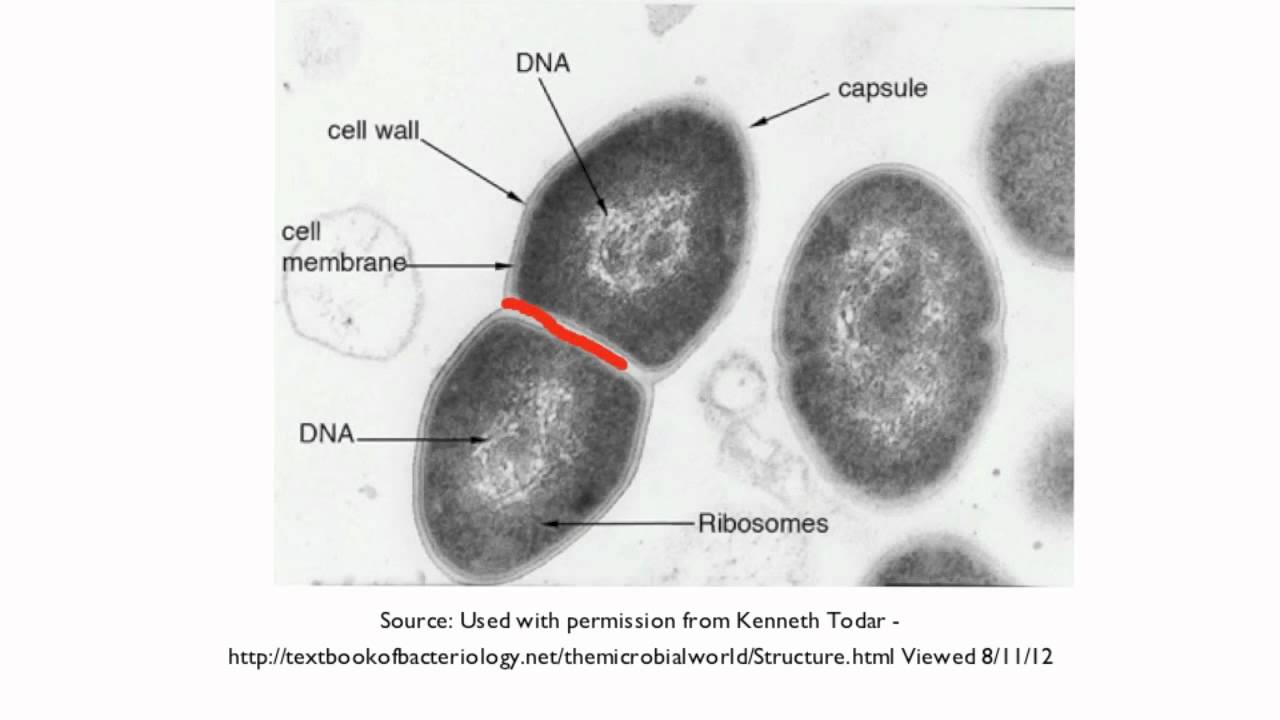
Inside the cyst, the nuclei undergo repetitive nuclear division followed by cytoplasmic division and result in the formation of amoebules. It covers itself in a protective covering and forms a structure known as cyst. Amoeba shows multiple fission under adverse conditions. In this method, the parent microbe divides into many daughter microbes. Multiple fission − Multiple fission is also seen in Amoeba. Finally, two cells are formed from one parent Amoeba. Each part receives a portion of the nucleus. This is followed by the division of the cytoplasm and the cell. In Amoeba,binary fission begins with the division of the nucleus. For example, Amoeba reproduces asexually by the process of binary fission. The reaction can be controlled or moderated by introducing a substance that absorbs neutrons before they can react with more uranium atoms.Asexual reproduction in unicellular organisms can be of three types:īinary fission: Binary fission is the splitting of parent organisms into two halves, each of which develops to form a complete daughter cell. Whether or not a chain reaction can occur depends on the energy of the neutrons that are released and how close the neighbor uranium atoms are. These two neutrons can go on to split other uranium nuclei, resulting in a nuclear chain reaction. In this particular reaction, one uranium nucleus breaks into a barium nucleus, a krypton nucleus, and two neutrons.

A common fission reaction produces barium-141 and krypton-92. The energy from the neutrons can cause the uranium nucleus to break in any of a number of different ways. In nuclear power plants, energetic neutrons are directed into a sample of the isotope uranium-235. Other times, energy is added to a nucleus to overcome the nuclear binding energy holding the protons and neutrons together. Sometimes this is supplied naturally, from radioactive decay of an element. For example, the fission of one kilogram of uranium releases as much energy as burning around four billion kilograms of coal.Įnergy is required in order for fission to occur. The energy released by nuclear fission is considerable. However, the daughter nuclei may still be radioactive. The mass change and energy release yield smaller nuclei that are more stable than the original heavy nucleus. The nucleus oscillates, so the repulsion may overcome the short-range attraction, causing the atom to split. The reason fission occurs is that energy upsets the balance between the electrostatic repulsion between positively-charged protons and the strong nuclear force that holds protons and neutrons together. Fission is a type of nuclear reaction that may occur spontaneously or as a result of a particle striking an atomic nucleus. The original heavy atom is termed the parent nucleus, and the lighter nuclei are daughter nuclei. Fission is the splitting of an atomic nucleus into two or more lighter nuclei accompanied by energy release.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
